8. HTTP Server Example Explanation#
1. Environment Preparation#
First, ensure that your CanMV development board is connected to a router or switch via an Ethernet port, and that the router is functioning properly and has internet access. This setup is a prerequisite for making HTTP requests.
2. Server Example Detailed Explanation#
Below is a simple HTTP server Python example based on the CanMV development board. This server listens on port 8081 and can respond to HTTP requests from clients.
2.1 Import Necessary Modules#
import socket
import network
import time
By importing the socket, network, and time modules, the socket module is used for network communication, network manages network interfaces (such as LAN), and time provides time-related functionalities.
2.2 Define Response Content#
CONTENT = b"""\
HTTP/1.0 200 OK
Hello #%d from k230 canmv MicroPython!
"""
Defines a byte string CONTENT as the HTTP response body. %d is a placeholder for a counter, indicating the sequence number of each request.
2.3 Define Main Function#
def main(micropython_optimize=True):
# ... (subsequent code)
Defines the main function, with the parameter micropython_optimize controlling whether to enable specific MicroPython optimizations.
2.4 Configure Network Interface#
def network_use_wlan(is_wlan=True):
if is_wlan:
sta = network.WLAN(0)
sta.connect("Canaan", "Canaan314")
print(sta.status())
while sta.ifconfig()[0] == '0.0.0.0':
os.exitpoint()
print(sta.ifconfig())
ip = sta.ifconfig()[0]
return ip
else:
a = network.LAN()
if not a.active():
raise RuntimeError("LAN interface is not active.")
a.ifconfig("dhcp")
print(a.ifconfig())
ip = a.ifconfig()[0]
return ip
This code selects between WLAN or LAN interface based on the is_wlan parameter. In WLAN mode, it connects to a specified Wi-Fi network, while in LAN mode, it obtains an IP address via DHCP. After obtaining and printing the network configuration, it returns the IP address.
2.5 Create and Configure Socket#
# Create socket object
s = socket.socket()
# Set socket options to allow address reuse
s.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1)
# Bind to all network interfaces, listening on port 8081
ai = socket.getaddrinfo("0.0.0.0", 8081)
addr = ai[0][-1]
s.bind(addr)
# Start listening, with a maximum of 5 connection requests
s.listen(5)
print("Listening, connect your browser to http://%s:8081/" % (network.LAN().ifconfig()[0]))
This code creates a socket and enables the SO_REUSEADDR option to allow port reuse. It binds the address and starts listening on port 8081, supporting up to 5 connection requests.
2.6 Handle Client Requests#
counter = 0
while True:
# Accept connection
res = s.accept()
client_sock = res[0]
client_addr = res[1]
print("Client address:", client_addr)
# Choose different reading methods based on whether optimization is enabled
if not micropython_optimize:
# Use stream interface (suitable for CPython)
client_stream = client_sock.makefile("rwb")
else:
# Use MicroPython-specific interface
client_stream = client_sock
# Read request content
# ...
# Send response
client_stream.write(CONTENT % counter)
# Close connection
client_stream.close()
counter += 1
time.sleep(2)
if counter > 0:
print("HTTP server exit!")
s.close()
break
The server main loop accepts client connections, selects different reading methods to handle requests, sends a response with a counter, and closes the connection. After closing the connection, it waits for 2 seconds before entering the next loop.
2.7 Complete Example#
import socket
import network
import time, os
CONTENT = b"""\
HTTP/1.0 200 OK
Hello #%d from k230 canmv MicroPython!
"""
def network_use_wlan(is_wlan=True):
if is_wlan:
sta = network.WLAN(0)
sta.connect("Canaan", "Canaan314")
print(sta.status())
while sta.ifconfig()[0] == '0.0.0.0':
os.exitpoint()
print(sta.ifconfig())
ip = sta.ifconfig()[0]
return ip
else:
a = network.LAN()
if not a.active():
raise RuntimeError("LAN interface is not active.")
a.ifconfig("dhcp")
print(a.ifconfig())
ip = a.ifconfig()[0]
return ip
def main(micropython_optimize=True):
ip = network_use_wlan(True)
s = socket.socket()
ai = socket.getaddrinfo("0.0.0.0", 8081)
addr = ai[0][-1]
s.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1)
s.bind(addr)
s.listen(5)
print("Listening, connect your browser to http://%s:8081/" % (ip))
counter = 0
while True:
res = s.accept()
client_sock = res[0]
client_addr = res[1]
print("Client address:", client_addr)
client_sock.setblocking(True)
client_stream = client_sock if micropython_optimize else client_sock.makefile("rwb")
while True:
h = client_stream.read()
if h is None:
continue
print(h)
if h.endswith(b'\r\n\r\n'):
break
os.exitpoint()
client_stream.write(CONTENT % counter)
client_stream.close()
counter += 1
time.sleep(2)
if counter > 0:
print("http server exit!")
s.close()
break
main()
For specific interface definitions, please refer to socket and network.
3. Example Phenomenon and Operation Instructions#
After running this example in the CanMV IDE K230, the IDE serial terminal will display the following information:
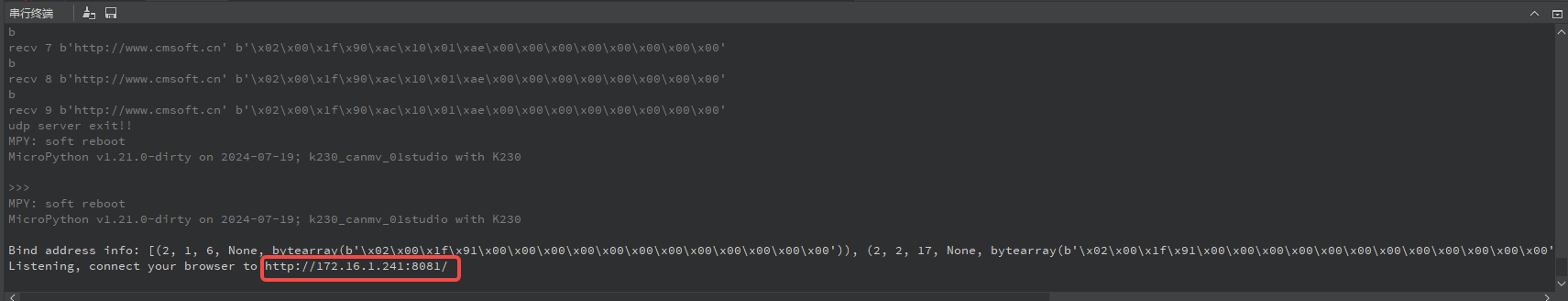
Copy the URL from the terminal and access it in your browser to view the server’s response:
